Underrated Ideas Of Info About How To Draw A Gene Map
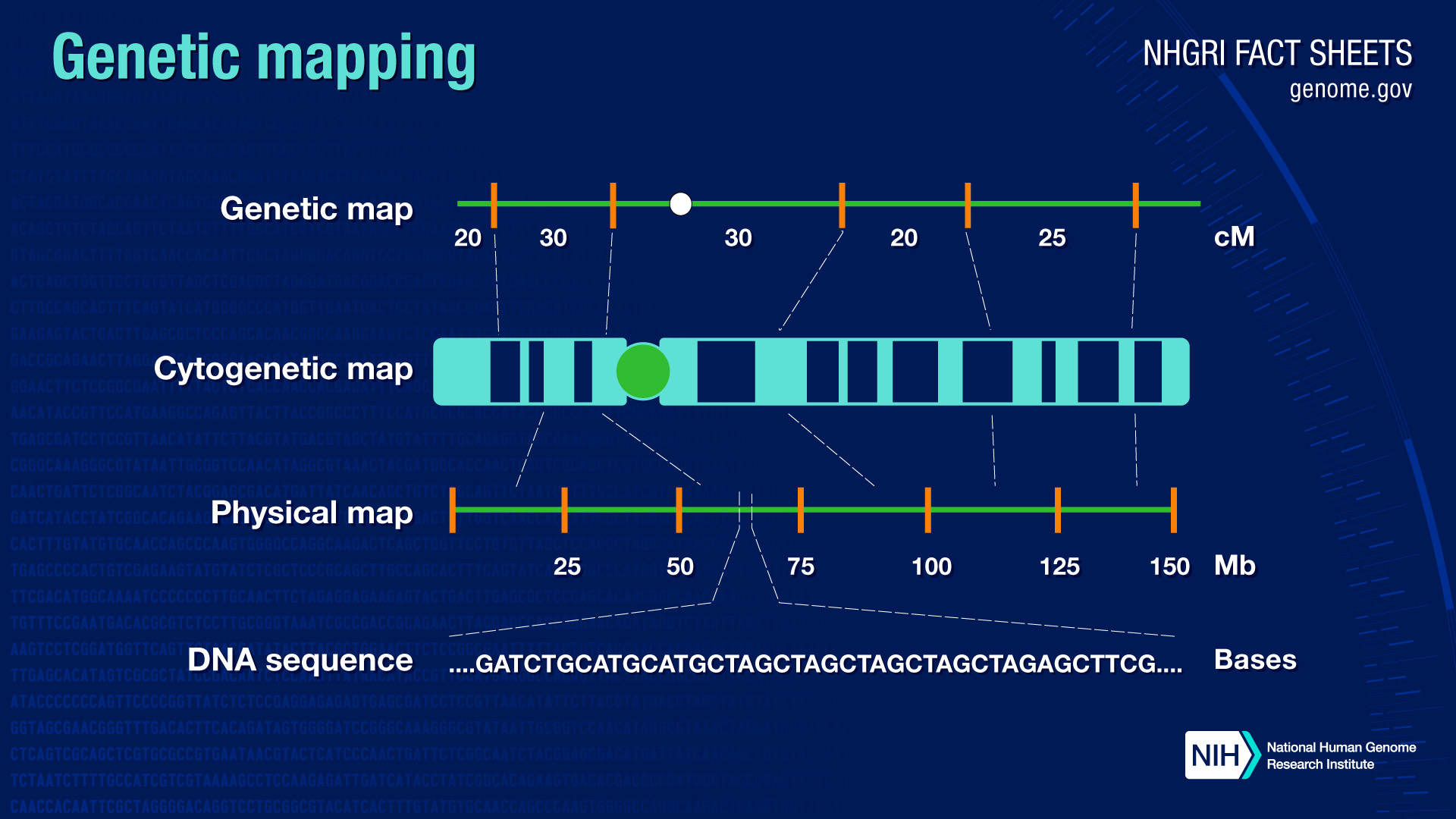
A physical map of the genome.
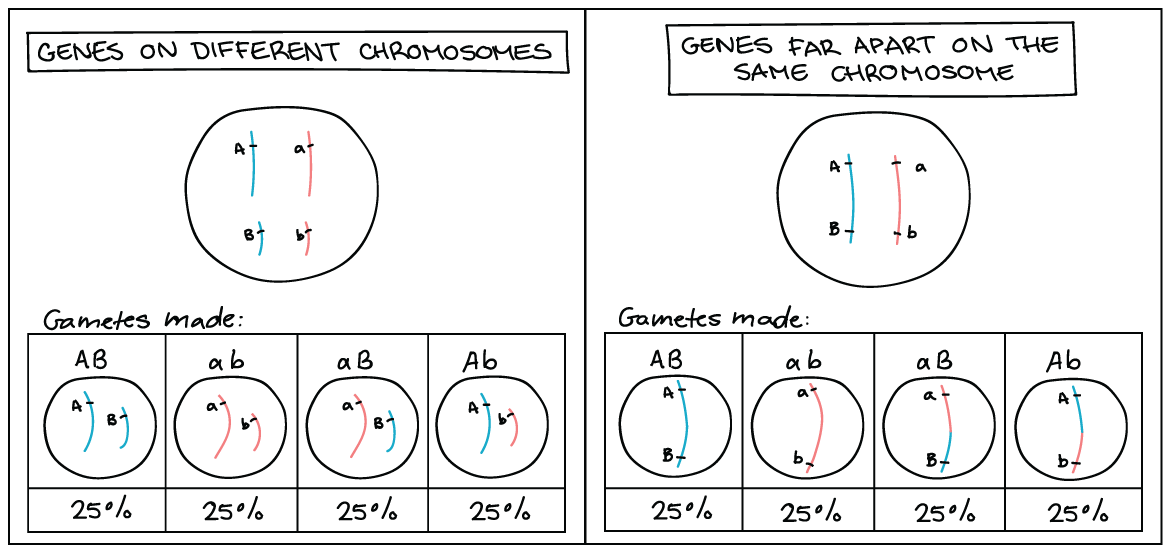
How to draw a gene map. Genes that are sufficiently close together on a chromosome will tend to stick together, and the versions (alleles) of those genes that are together on a. Svg container, single chromosome container, chromosome, chromosome id, gene. A genetic map (also called a linkage map) shows the relative location of genetic markers (reflecting sites of genomic variants) on a chromosome.
The drawing of a genetic map is decomposed into 8 modules inmg2c program as follows: Ggplot (example_genes, aes (xmin = start, xmax = end, y = molecule, fill = gene, forward = orientation)) + geom_gene_arrow () + facet_wrap (~ molecule, scales = free, ncol = 1) +. The genome map provides a graphical.
An object of class sequence with a predefined order, linkage phases, recombination fraction and likelihood; Gene maps can be drawn to different degrees of resolution, or detail. To display a genome map select a genome in the “ virus selector ” and in the “ draw ” menu select “ genome map “.
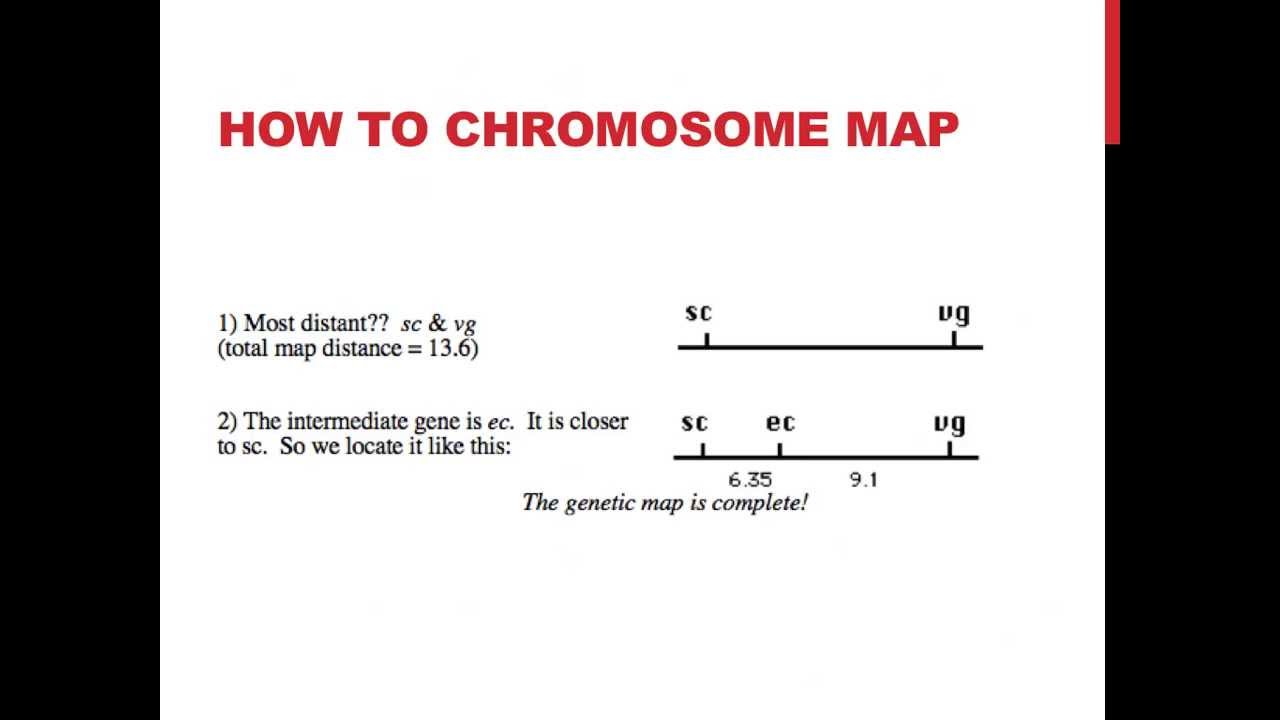
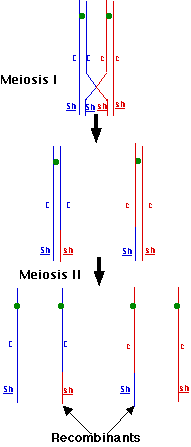
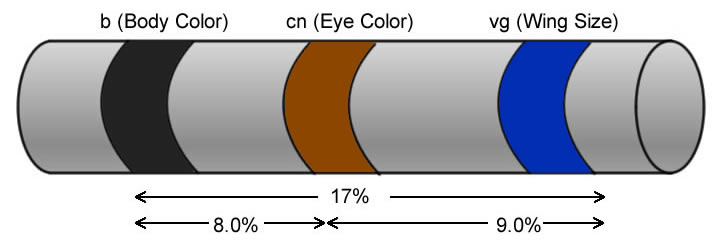
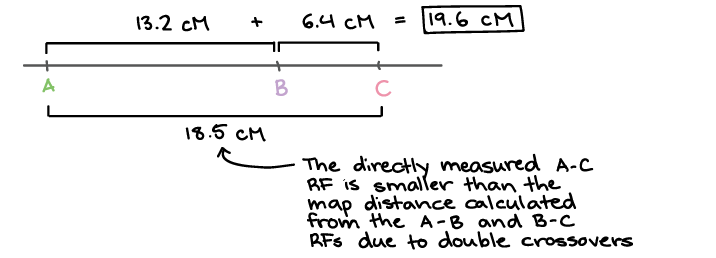
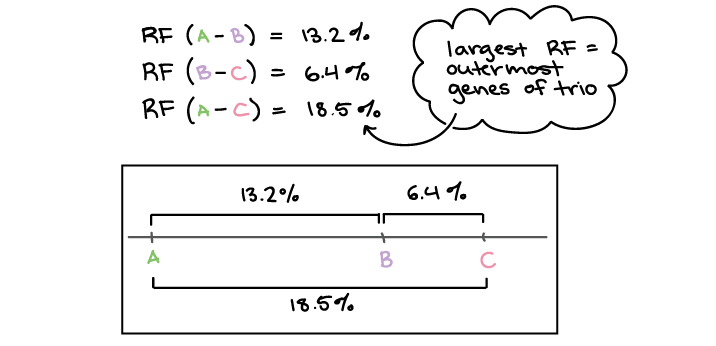
Also it could be a list of maps. Draw the correct positions of the genes relative to each other and. Linkage maps are basically, a kind of “road map” of the chromosomes drawn based on segregation pattern of markers.
The size of the gene model, aka the height of the polygons. Just as you might describe the location of your own home as part of a particular planet, continent, country, city, or even. The content of the article is structured as follows:
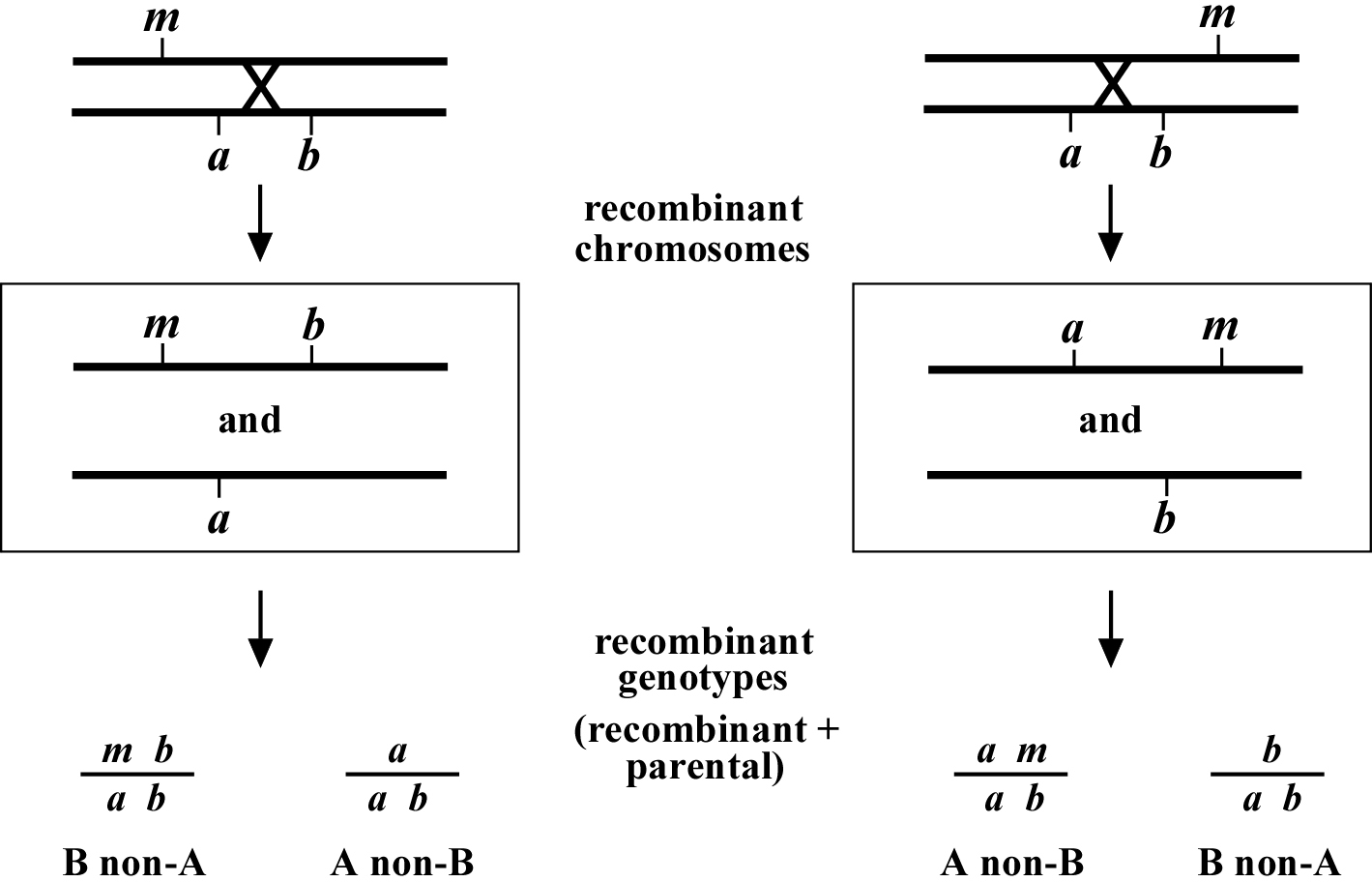
In some cases, the answer is yes. D morgan pave the foundation of gene map by. They indicate the position and relative genetic distances.
In this post you’ll learn how to draw heatmaps in the r programming language. Here is how you draw a gene scheme in illustrator for your graphical abstract.software: In this video paul andersen explains how the frequency of recombination between linked genes can be used to determine the relative location of genes on a chr.
Draw a map of the chromose these two genes are found on, including the centromere, and both genes.